A guest post
Over the last couple of weeks, it has been my great pleasure to assist Chip Zoller in writing a VMware PowerCLI script, named Optimize-VMwarePKS. This script helps organise your PKS deployment at three levels: folders, tags and DRS rules, including functionality to run a clean up.

The following post by Chip describes the function in greater detail, and shows how you can use it.
This post also appears on the Sovereign Systems website as Optimize-VMwarePKS: A PowerShell Script for All Your VMware PKS Deployment Needs.
Take it away Chip.
Optimize-VMwarePKS: A PowerShell script for all your VMware PKS deployment needs
Ever since VMware PKS (now called Enterprise PKS) came onto the market over a year ago, it’s been a big hit. With it, you get upstream Kubernetes, NSX-T, an enterprise-class container registry, automation of the entire K8s cluster creation process, and lots more all on top of the de facto private cloud platform of vSphere. It’s truly becoming the way organizations are standardizing on K8s cluster instantiation, upgrade, and management on-premises. The deployment nodes themselves are regular virtual machines. And, like all virtual machines, you and your company probably have an established way of organizing those VMs. While Enterprise PKS takes care of a lot of tasks automatically, one thing that we still need to consider is how those VMs get organized. So, as a joint effort between myself and Luc Dekens, we’re glad to announce today a new script called Optimize-VMwarePKS which is designed to bring that level of optimization to your vSphere and PKS clusters. Specifically, this script is designed to optimize your PKS deployments in three ways: vSphere folders, vSphere tags, and DRS rules–with clean-up for three of these. Read on to see this in action and learn how you can greatly simplify deployment of PKS clusters in your own environment.
FOLDERS
As mentioned, PKS deploys K8s nodes as simple VMs into your vSphere environment. After a single deployment, you may see something like this in your vSphere Client.

All VMs are, as you can see, named with IDs that are doled out by PKS and BOSH, and tracked internally. They probably look very different from the internal naming standard you’ve developed, right? Although we shouldn’t change the names of the VMs, we can do other things. The first feature of Optimize-VMwarePKS is the ability to place all VMs from a given deployment automatically into a folder based on that name. In so doing, the above screenshot now looks like this after optimization:
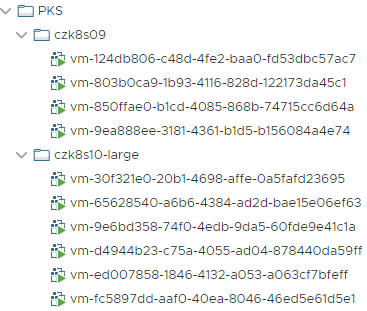
As you can see, these folder names align with the PKS cluster names perfectly if we examine them with a pks clusters command. In fact, Optimize-VMwarePKS is designed to take this information directly from the PKS CLI tool, which is a requirement for the script (see later).
The nice thing about this script is
- it’s very easy to operate (simply add the –ProcessFolders switch)
- it’s idempotent so will keep this organization no matter how many times you run it.
TAGS
The second feature of Optimize-VMwarePKS to highlight is the ability to assign vSphere Tags to all of the VMs that form a given PKS deployment. Tags are often used to provide a form of organization that may exist alongside or independent of vSphere folders. These tags are, again by default, created based on the name of the PKS cluster and automatically created and assigned to all VMs part of a cluster. With a tag category of your choice (or by accepting the default category of ‘PKS’), the script will detect your clusters, create a new appropriate tag in the tag category, and assign that tag to all VMs.
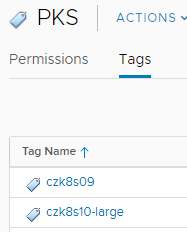
As you can see here, the script has created two tags for us that match the names of our clusters. If we inspect the VMs within those clusters, we can see it’s been correctly assigned as well.
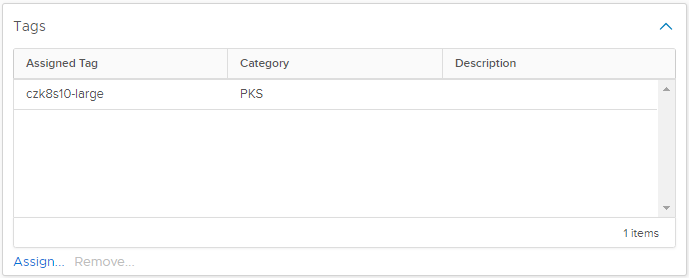
This optimization is easily enabled with the -ProcessTags switch.
DRS RULES
Since PKS has the ability to deploy HA K8s clusters–which is a tremendous strength and huge time saver–it automatically provisions multiple masters and places them behind an NSX-T load balancer. These masters then serve as the API entry point for all K8s-related commands. Masters can be spread out across multiple Availability Zones (AZ). Where AZs map directly onto distinct vSphere clusters, this provides a sufficient level of fault isolation. But in the case where either multiple Azs aren’t in use or they do not align to separate compute clusters, Enterprise PKS will place all masters on the same cluster. Optimize-VMwarePKS can therefore be used to build DRS anti-affinity rules to provide such separation.
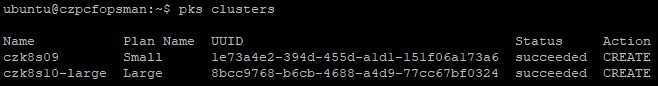
In my previous screenshots, you’ve noticed I have a single small cluster (1 master; 3 workers) and a large cluster (3 masters; 3 workers). If we run the script with the -ProcessDRSRules switch, it will automatically find those masters and create a DRS anti-affinity rule for us. And not to worry, it’ll only create the rule with the masters of each cluster, so multiple HA clusters get individual DRS rules created. See below. Even better, the script is written in a future-proof way in that when VMware/Pivotal support larger multi-master clusters in the future, if you scaled out masters the script will detect the increase and update the rule for you!
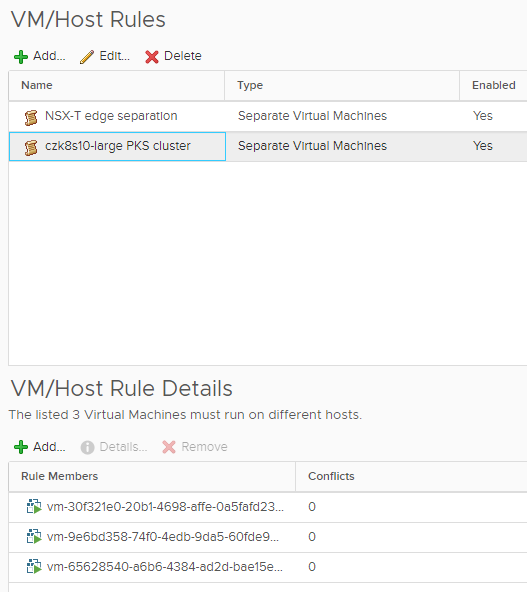
These abilities are, as I hope you’ll agree, extremely useful in order to not only fill some gaps but bring VMware PKS deployments into alignment with your vSphere policies today. But there’s one thing missing that we haven’t covered yet. Kubernetes clusters may come and go (another big win for Enterprise PKS is the automatic roll-back of NSX-T objects!), and when they do we want to ensure we aren’t leaving behind elements that are no longer relevant. So the last portion of Optimize-VMwarePKS is its ability to automatically maintain a tidy house.
TIDYING UP
Each of the three optimizations shown previously (folders, tags, and DRS rules) can be switched on independently. And with each one, except DRS rules, if a cluster gets deleted we’d have some clean-up work to do. So the script has also been written with switches that you can (optionally, of course) automate the clean-up of these objects. We’re talking here about tidying up of vSphere folders and vSphere tags. By adding the -TidyFolders and/or -TidyTags switches, Optimize-VMwarePKS will search for these empty folders and tags and remove them for you. But, not to fear, it will *only* do this if you’ve provided these switches and also only consider the parent vSphere folder or tag category for clean-up. That means it won’t scour your entire estate and remove anything else.
IDEMPOTENCE
Lastly, and before we look at some running examples, is to point out the idempotent nature of this script. Because you may have many groups of people bring up and down PKS deployments, you need something that can maintain a ready state of what you define, similar to tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef. Being able to schedule this script is one of the main reasons it was written, and in so doing it must be made idempotent. No matter how many times you run the script, it always checks if things exist before making a change. You can be confident that when you ask it to run with whatever parameters that it’ll maintain that state exactly. So no fear if someone drops a tag or moves a VM out of a folder. Next time it runs it’ll put it right back where it was.
RUNNING OPTIMIZE-VMWAREPKS
Now you’re aware of all its capabilities, let’s quickly look at what’s needed to run it and then an example on how to run it.
The script needs PowerShell, VMware PowerCLI, and the PKS CLI binary tool, all of which are cross-platform at this point. In fact, it has been tested running directly from the Pivotal Operations Manager appliance running Ubuntu with PowerShell Core but runs perfectly fine from a Windows control machine as well. The PKS CLI tool needs to be added to your PATH. You also must ensure you have credentials and network connectivity to access both vCenter Server and PKS.
Now you have the prereqs, time to actually run this script. Grab it from the GitHub repo here. For your convenience (and so you don’t have to either read a blog or inspect the code), extensive help has been provided on how to operate the script, its parameters, but some examples.
All the switches can be run independently, so you can mix and match whatever functionality you like and only it will run. If we want to let it process folders, tags, and DRS rules for us, we could call it like so:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
$secvCPass = ConvertTo-SecureString -String 'VMware1!' -asPlainText -Force $credvC = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('administrator@vsphere.local',$secvCPass) $secPKSPass = ConvertTo-SecureString -String 'VMware1!' -asPlainText -Force $credPKS = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('myuser',$secPKSPass) ./Optimize-VMwarePKS.ps1 -ProcessFolders -ProcessTags -ProcessDRSRules -vCenter $vc -vCenterCredential $credvC -PKSSever $pks -PKSCredential $credPKS -Verbose |
We have to pass a PSCredential object to the script, and so the lines before actually running it do that for us.
If all you wanted was to clean-up (tidy) those objects, run it with only those flags set:
|
1 |
./Optimize-VMwarePKS.ps1 -TidyFolders -TidyTags -vCenter $vc -vCenterCredential $credvC -PKSSever $pks -PKSCredential $credPKS |
Or, combine all flags into a single command:
|
1 |
./Optimize-VMwarePKS.ps1 -ProcessFolders -ProcessTags -ProcessDRSRules -TidyFolders -TidyTags -vCenter $vc -vCenterCredential $credvC -PKSSever $pks -PKSCredential $credPKS |
As far as managing the parameters needed, one of the most convenient ways is with splatting in PowerShell. We can write a script, call it “wrapper.ps1” and put all parameters inside of it as shown below. Note that with splatting, we must set the values to “true” unlike when passing the switches to the script directly. The final line simply calls Optimize-VMwarePKS for us passing the entire splat as an argument.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
$vCUser = 'myuser@mydomain.com' $vCPass = 'VMware1!' | ConvertTo-SecureString -asPlainText -Force $PKSUser = 'myuser' $PKSPass = 'VMware1!' | ConvertTo-SecureString -asPlainText -Force $params = @{ ProcessFolders = $true ProcessTags = $true ProcessDRSRules = $true TidyFolders = $true TidyTags = $true vCenter = 'myvcenter.mydomain.com' PKSServer = 'mypks.mydomain.com' vCenterCredential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential($vCUser,$vCPass) PKSCredential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential($PKSUser,$PKSPass) } /home/ubuntu/Optimize-VMwarePKS.ps1 @params |
And, as mentioned earlier, because this script is entirely idempotent, it can easily be scheduled with either cron, Windows task scheduler, or any other mechanism you want. This will ensure your environment is kept optimized based on your rules and patterns with no manual clean-up required.
I hope you find this script to be valuable in your environments. If so, we’d love to hear about it and you can drop either Luc or Chip a line on Twitter at @LucD22 or @chipzoller respectively.
Thanks Chip.
Enjoy!

Paul Dillon
I read that the script will work against every PKS created vm existing in VMWare.
1. Can you confirm my understanding of the scope of impact for this script?
2. For instance, is there a way to limit the scope to a single SDDC in VMWare?
LucD
Hi Paul,
Thanks for the feedback. On your questions
1. The script will work against all VMs under the PKSCluster you specified. These are not necessarily all PKS VMs if you have multiple PKS clusters.
2. Not exactly sure what you mean with SDDC here, but you limit the scope of the script with the afformentioned PKSServer parameter.
Chip Zoller
Thanks for bringing up that idea. A couple reasons, mainly, but there are others depending on how customers like to consume things.
1.) This script, because idempotent and if run on a schedule, will ensure ready state is maintained in case a user removes a tag or changes folders inadvertently. It’ll also allow scaling out of masters to update the DRS rule.
2.) Easier visibility since VM extensions have to be created against the API directly.
3.) Quickly modified and extended if other functionality is later desired.
AdaptiveThinking
I’m not sure why you would use Powershell outside of PKS (Opsman) for that.
It would be a lot better to just use the BOSH VM Extensions for DRS, Folders and Tags.
If you do that, BOSH (=PKS) would automatically create all that for new VMs and delete it if it deletes a VM.